Based on any house lies the foundation. For the construction of residential buildings in the private sector, in most cases, the basement of the foundation laying is used. However, in each particular case, individual calculations of the base, taking into account the mass of factors, starting on the characteristics of the soil, ending with the weighing of the building built and the climatic conditions of the region. And special attention requires the lower part of the base, in contact with the soil - the sole. In this article we will talk about calculating the soles of the tape basement.
Content
Why do you need the calculation of the sole
The foundation of one house is able to rely on the soil with a different bearing ability. This ability is the force with which the weight of the building puts on the ground and implies not only the mass itself, but also the period of time that passes before the soil begins to deform under pressure. In the traditional sense, the sole of the ribbon foundation looks like a reinforced concrete platform, the main task of which is the uniform distribution of the load entering the ground from the building. The carrying capacity of the soil is indicated by the letter R and are measured in tons per 1 m³.
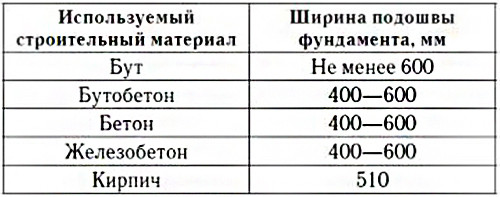
The width of the ribbon basement, as a rule, at least twice the width of the foundation itself, which is explained by the design itself. The sole is necessary for most building local standards and the requirements for the installation of foundations on unstable soils (or strong, loose, sandy).
The calculation of the sole is necessary in order for its widths and thickness of the drainage layer under it enough to withstand the load from the house. As a result, the specific mass of the building should be less than the calculated resistance of the soil.
Before proceeding with the design and calculations, it is necessary to collect a lot of data regarding geology, geodesy and hydrogeology of the site. Calculations directly depend on the level of groundwater, chemistry and soil physics, the characteristics of the landscape. Also a significant role is played by the environmental situation and the degree of construction of the territory. So, if you have at home nearby, you can take advantage of the experience of early developers and save time.
So, the size of the soles of the ribbon foundation is determined by either the degree of shrinkage of the soil, or by its bearing ability. The last method is more popular because it does not require professional knowledge and skills.
How to determine the type of soil
To calculate the sole of the foundation, it is necessary to repel from the loads that this is the most foundation will be exposed. Along with this, the sole will evenly distribute these loads throughout its area, reducing a possible minimum negative impact on the soil. Therefore, in order to correctly fulfill the calculations, you need to know the characteristics of the soil. Since geologists' services are quite expensive, and to resort to them during the construction of small private houses is not always appropriate, we suggest learning to independently determine the properties of the soil on your site.
First, you will need to dig a well with a depth of 2.5 m and the width of approximately 80x80 cm. Deliching every 50 cm, take the soil sample and be sure to mark on the bank where the sample linked.
When 5 trials were taken and the depth of 2.5 m was achieved, you can proceed to tests that determine the type of base:
- The sample of the soil is abundantly moisten with cold water, roll out the palms of 12-15 mm harness in diameter 10-15 cm long and maintain it into the ring. If at the same time the harness will crumble on small pieces, it means that it can be argued that at this depth (see the labeling on the bank) are predominantly sandy. If the harness crouches into several large fragments, it means that there are loams in the designated depth. And if you succeed, bend harness to the ring and not damage it, then you will have to build a house on a clay base.
- The second testing allows you to determine the porosity of the soil. Cut out the cube with a side of 10 cm and weigh it. The mass of the earthen cube indicates the bulk weight of the soil in the natural state. Seal the cube, squeezing with his fingers as much as possible, and again weighing to determine the weight of the earth without air. The ratio of the volume of soil samples to the mass denotes volumetric weight in normal and dense. The porosity coefficient is obtained from the ratio of the volume mass of two cubes ("to" and "after"). Looking at this coefficient, you can determine the intended type of base. If when you cut a cube or squeezed it, it collapsed into pieces, then the amount of soil with airpasses is understood by the size of the cube, and the volume without pores can be calculated using a measuring cup or other capacitance.
- Another test is on the soil fluidity. It can be determined so: if the shovel is difficult to drive into the soil, then the fluidity is zero. If she immediately entered, but the land towards it greatly, it means that the fluidity is equal to one.
These tests help determine the possible characteristics of the ground base. In order to insure itself from fatal errors, the resistance of the soil can be slightly overlapping with respect to the value obtained for your site. In the event that the results did not give any clear answers, or the Earth was too pumped, it means it is better to use the services of professional geodesists.
We make calculations
The calculation of the basement soles occurs in several main stages. At first it is necessary to find the weight of the future structures, including the mass of the walls, roofs, coatings, etc. This also includes snow and payload, specific pressure. Consider this process in all details.
Weight calculation
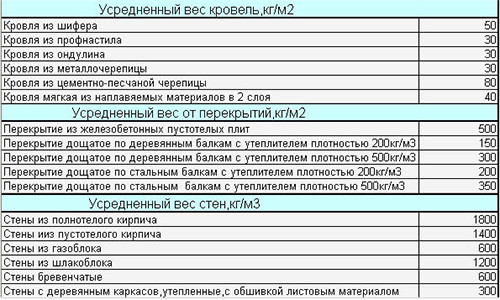
To find out the most accurate weight, you need to figure out the mass of all elements of the future building. Any house consists of a foundation, basement floor, floor overlaps and ceiling, walls, including inner partitions, windows, doors, roofs (rafter system, pie), etc. It is clear that to calculate the mass of each element, it is necessary to represent which it will be the sizes and from which materials will consist. Walls, for example, include not only brick, wood or concrete, but also the heat insulating layer, inner and exterior decoration. That is why it is so important to make detailed sketches and plans.
If one of the elements of the building has a rectangular shape, its volume can be calculated very simply, moving length to height and width. With more bizarre forms, it is not so easy, but also quite understandable - they need to "disassemble" to simpler forms (triangles and rectangles), find out the volume of each part, after which summarize the results.
The specific mass of each element is determined by the material from which it is made. The indicators of traditional building materials are listed in SNiP II-3-79, but referring to any SNiP, it should be taken into account that these regulations were spelled out for quite a long time. Since then, the construction industry has made several large steps forward, so the data of the manuals can serve only additional sources of information. Today there are many modern materials on the market, which at high strength have a small specific weight. They are not listed in SNiP, so all the information should be recognized by the manufacturer.
If you build a house from the elements of the standard form, for example, foam blocks, bars, etc., you should refer to the regulatory documents, where the weight of each element is specified. Knowing the number of blocks or bars and the mass of each of them can be easily calculated at home.
Since when calculating should also consider the weight of the foundation, its initial parameters should be known. In the future, they can be corrected in accordance with the results of calculations. This should establish exemplary sizes and select the material for the manufacture of the future base. The choice of material depends on the characteristics of the soil, the depth of the water, the depth of the freezing point.
The volume and mass of the foundation can be treated by analogy with the volume and mass of other elements of the building. In this case, it should be remembered that the determining point of the calculation is the width of the sole, because it depends on it the degree of influence of the box of the house on the ground.
Load calculation
The pressure on the ground every year is intensified with snow load, which is especially noticeable in the northern regions, where a lot of snow falls out every winter. To determine the snow load, you need to multiply the area of \u200b\u200bthe roof on the characteristics of the mass of snow cover (these parameters are written in SNiP 2.01.07-85).
It is useful to know: when calculating snow load, it is necessary to take into account the angle of inclination of the roof. So, if the roof is flat, the snow on it will delay and accumulate, giving a greater load. If the angle of inclination is big, the snow will not be able to delay on the surface, respectively, the snow load will be minimal.
At first they calculate the snow load, and then the correction coefficient is made depending on the angle of inclination of the roof and the number of skates. If the angle of inclination is less than 25 °, the correction coefficient will be equal to one, if the angle is greater than 60 °, the coefficient will be zero. In the range from 25 ° to 60 ° it will be extrapolated between 1 and 0.
There is also a payload that includes a mass of furniture, all household items and tenants themselves. Calculate such a value exactly simply unrealistic, therefore there was averaged value of 180 kg / m².
When you found the weight of all components of the future building, you can determine the total weight of the house and the load on the foundation. In the process of the distribution of this mass on the area of \u200b\u200bthe sole, it turns out the specific pressure on the soil (calculated in t / m²).
Size calculation
The guarantee of the quality and durability of any foundation is a state at which the specific house pressure was below the calculated resistance of the soil. We have already said that the calculated resistance is the value at which the soil is not deformed under load. The corresponding values \u200b\u200bfor all regions of Russia can be found in DBN B.2.1-10-2009 "The foundations and foundations of structures". As you have already conducted tests and know the characteristics of the soil, you can determine the calculated resistance according to the standards.
Resistance for different soils:
- coarse sand - 60-50 tons / m²;
- mediterranean sand - 50-40 tons / m²;
- sacks - 30-20 tons / m²;
- suglinka - 30-10 tons / m²;
- clay - 60-10 t / m²;
- crushed stone - 60-40 tons / m²;
- gravel - 50-35 tons / m².
If in your case the calculations show that the resistance is greater than the load of the house, it means that everything is correct. It is recommended to ask a certain margin of the strength of the base. To do this, it is necessary to make the resistance to be larger by 15-20%. If the results have shown that it is less or equal to the load, then the sole must be expanded, after which it is re-made everything. And on the contrary - if the resistance is more load, the sole should be reduced. This will save on building materials and labor costs. Recalculating everything in a new way, remember that due to the reduction of the sole size, its volume and weight will decrease.
Strengthening soles
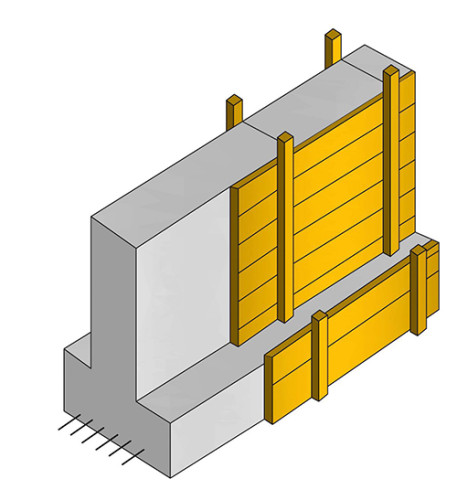
During the operation of the house, it is often the strengthening of its foundation. This may happen due to the growth of loads, damage or insufficient carrier of the soil. Over time, the characteristics of the soil may vary, accordingly, their carrying ability changes. One of the most effective measures to strengthen is the broadening of the ribbon foundation soles, that is, an increase in its size. As a result, part of the load from the existing foundation will be transmitted to reinforcement elements - reinforced concrete plates, monolithically associated with the existing foundation by means of reinforcing frame.
To increase the sole of the foundation, first in his body do the holes in the chess order, where metal pipes are installed. The reinforcement frame is attached to these pipes with welding, put a formwork and poured concrete. Reinforcement of the ribbon foundation soles should be carried out in any case, regardless of loads and the degree of soil resistance.
Calculate the sole and other parameters of the belt foundation are absolutely necessary, but this work requires extensive construction knowledge, including different areas. Therefore, if you are not sure about your abilities, you can independently perform preparatory work (determine the type of soil and snow load, for example), and the rest is instructed to specialists.