The rafter system is an integral element of any roof. Its main task is to maintain roofing pie and confronting external loads. The design of the rafter system depends on many factors, ranging from the weight of the roof itself, ending with climatic conditions of the terrain. Its correct calculation determines the durability of the design and comfort of residents at home. In this article we will talk about calculating the rafting roof system.
Content
Materials for building
To build a high-quality rafter system, it should be remembered that this engineering structure should protect the building from environmental exposure for many years. That is why the construction material must be as strong as possible and durable. At the same time, the "skeleton" of the roof must have relative ease so as not to increase the already strong loads.
The optimal and most common material for the construction of the rafter system is a tree. With due process, it is capable of listening to several decades, and with proper installation of roofing pie (hydro and vaporizolation), such a roof may simultane from 70 to 100 years without overhaul.
The advantages of wooden rafters:
- Easy to manufacture.
- Easy installation.
- The possibility of adjusting rafters at the installation site.
- Low cost.
Compared to reinforced concrete or metal rafting systems, the tree wins in all respects.
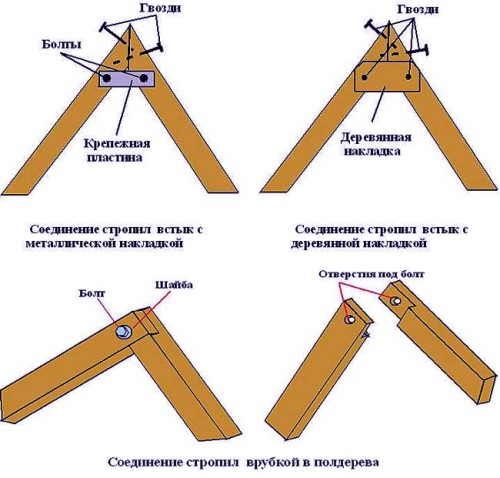
Fasteners for the rafter system
To impart stability and fortress, the elements of the rafter system are tightened with various fasteners - bolts, self-stakes, nails, clamps and brackets. Many specialists prefer not to use nails or apply them in minimal quantities, since such a type of connection is least durable. When building a "skeleton" of the roof, reliability and durability are very important, even in the smallest details, and since the wood is typical with time to dying, then places bonded by nails begin to break and need to be repaired.
Also, roofer specialists do not recommend using bolted connections, since they need special holes for them. These holes reduce the stability and strength of the entire design.
The most reliable fastener for connecting rafted among themselves is brackets and clamps. Also, many firms offer the services of manufacturing a rafter skeleton in industrial conditions, providing a long-term warranty to the customer. As a rule, for the connection, fasteners are used there, which firmly fix the rafters and increase the stability of the entire design.
Loads on the roof
No house is impossible to build without a foundation, otherwise he will just justify. The foundation holds the walls of the house of the house, distributes the load and does not allow the building to move or fall into the ground. The rafting system is a "foundation" for roofing pie, and without it the construction of the roof is unacceptable. Depending on which the materials will be roofing (thermal insulation, waterproofing, external coating) depends on the strength of the "skeleton".
Also, the nature of the design also affects the nature of the design, for example, the calculation of the rafter system of the two-tie roof is not suitable in the case of the construction of a four-piece or attic roof. Therefore, at first, a preliminary drawing of the house should be made, and only then proceed to calculations.
And if everything depended on personal preferences and designer ideas, it would be much easier, but an influence of not only the weight and shape of roofing cake affects the rafter system. There are a number of loads that do not depend on humans.
Conditionally all types of loads on the rafter system can be divided into three categories:
- Permanent - to permanent loads include the weight of the roof, overlappings, crates and all components of the cake. Also, if some equipment is installed on the roof, or you plan to make an exploited flat roof, green roof, it should be considered.
- Temporary - these loads include the weight of snow falling in winter, fallen autumn foliage, rainwater, etc. This category directly depends on the climatic zone. So, if you build a house in the south, where there is practically no snow, the load will be less than if you were built a house in the north of the country, where a snow layer of half the roof can accumulate on the roof.
- Specific - under this category are housed houses built in seismically dangerous regions, zones of regular emergence of hurricane winds, tornado, etc. The charter system in these cases must have an additional margin of strength.
To correctly calculate the rafter system, you should consider all the smallest details and factors that affect the roof. Therefore, we consider in more detail the full list of loads.
Loading snow on the roof
All loads, including snow, are calculated by special formulas. We will give a simpler and "fast" of existing ones. Immediately, it should be noted that today on the Internet you can find special online calculators or programs to calculate any types of roof loads, taking into account the location of the house on the map.
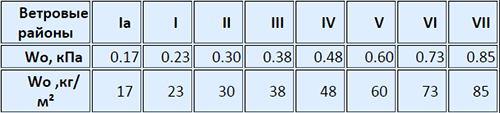
So, to calculate the snow load, use the formula: S \u003d μ * SG
S - Snow load data measured in kg / kV. M to find, μ is a coefficient that is determined by the roof slope, SG is a snow load in kg / sq. M, which is characteristic of a particular region of the country, α (alpha) - the value indicating the slope of the roof and expressed in degrees.
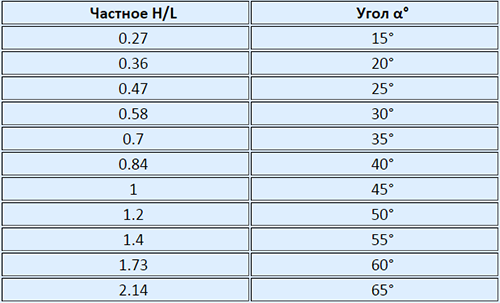
To learn an exemplary bias of the roof, divide its height (H) to ½ span (L). Results can be viewed in the table below.
If the inclination of the roof is 30 ° or less, then μ will be equal to 1, with α at 60 ° or more μ \u003d 0.
Suppose, 30 ° \u003cα \u003c60 °, then μ \u003d 0.033 · (60-α).
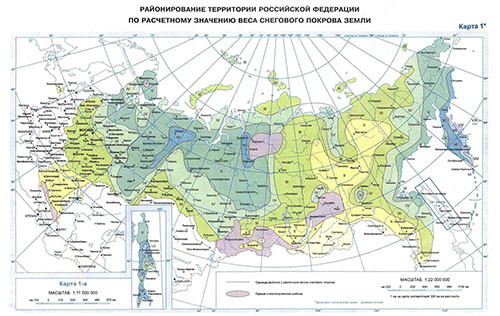
To find out the SG snow load characteristic of the selected region, use the SNiP application 2.01.07-85 or take a look at the road map of the Russian Federation.
The map shows districts from 1 to 8 and the snow load for each of them in kg / sq. M (the higher the higher the number, the closer to the north of the country there is a region, therefore, the snow load is stronger):
- 1 - 80 kg / sq. m;
- 2 - 120 kg / square meters. m;
- 3 - 180 kg / kV. m;
- 4 - 240 kg / kV. m;
- 5 - 320 kg / kV. m;
- 6 - 400 kg / sq. m;
- 7 - 480 kg / sq. m;
- 8 - 560 kg / kV. m.
Let us calculate the maximum permissible burden of snow on the roof of the house, which is in the village of Babenki in the Ivanovo region. The height of the roof is 2.5 m, and the length of the span is 7 m.
If you look at the map, you can calculate the nominal snow load peculiar to this region, that is, SG. For Region No. 4, it is 240 kg / kV. m.
Now it is necessary to find α (the angle of the slope), dividing the height of the roof on ½ of the span: 2.5 / 3.5 \u003d 0.714. Now the table is easy to determine that α \u003d 36 °.
It follows from this that 30 ° \u003cα \u003c60 °, therefore, to calculate μ, we use the formula μ \u003d 0.033 * (60-α). Since α \u003d 36 °, then the calculation will look as follows: 0.033 * (60-36) \u003d 0.79.
Now we have all the data in order to calculate the maximum snow load: 240 * 0.79 \u003d 189 kg / kV. m.
Load wind on the roof
If you build a cool roof with a slope greater than 30 °, then because of the large sailiness, the wind will put very much from the side, and the roof will experience serious loads. With a canopy of a skate up to 30 °, lifting aerodynamic force will be involved - the wind will ride the roof, creating turbulence under the sinks, as a result of which the roof will try to take off. It is for such a principle that airplanes work.
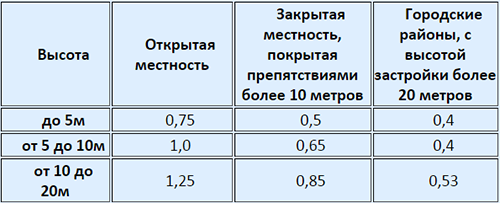
Snip 2.01.07-85 offers a formula for calculating the value of the average wind load at the level above the ground surface (Z): WM \u003d WO * K * C, where WM is a wind load, WO - wind pressure peculiar to one or another region of the country (Regulatory pressure), K is a coefficient that takes into account changes in the wind pressure depending on the height above the ground level.
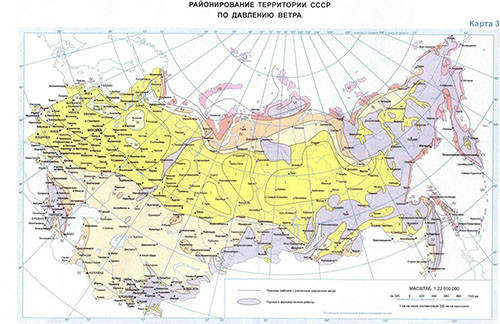
You can view the normative wind pressure on a special map below or in Appendix 5 SNiP 2.01.07-85.
The coefficient of changes in the wind pressure in height (K) is listed in the table and depend not only on the height of the structure, but also on the characteristics of the area and the landscape.
The letter C will subsequently be denoted by the coefficient of aerodynamic force, depending on the configuration of the house and the roof itself. It may vary from -1.8 (the roof is trying to "take off") to +0.8 (the wind gives great to the same sides of the high roof and tries to overturn it). Since we use a simplified calculation as an example, it will be 0.8.
Useful advice: Since the strength of the wind, which seeks or tilt, or snatch the roof, can reach impressive power, the lower part of each of the rafter feet should be attached to the wall or matrix. It can be done anything, for example, softened on the heat of steel wire 5-6 mm in diameter. Screw each leg with such a soft wire to the slabs of overlapping or matrices.
Based on how the wind can affect the roof, it suggests a logical output - than the roof is harder, the better. The heavy roof will be more difficult to overturn or tear off from the rafted, but the increase in the weight of the roof should entail the strengthening of the construction system.
For example, we will make calculation of the rafter system of the attic roof, which is located 6 m from the ground, and the angle of the slope is 36 °. Building is all in the same village of Babenki.
Judging by the map of the nominal wind load, WO \u003d 30 kg / kV. m.
Since there are no buildings in the village above 10 m, then K \u003d 1.0
With the value of the aerodynamic effect coefficient +0.8, we calculate the average wind load by the formula: WM \u003d 30 * 1.0 * 0.8 \u003d 24 kg / kV. m.
It is useful to know: if the wind will blow into the end of our roof, then the raising force will affect its edge with a capacity of up to 33.6 kg / sq. m.
Weight of roofing pie
This factor relates to the category of permanent loads and does not depend on the location of the house, and on what materials were used for the construction of the roof.
Each roofing coverage has its own permanent weight:
- slate weighs from 10 to 15 kg / square meters. m depending on the thickness and quality;
- bituminous slate (Ondulin) weighs and has a load from 4 to 6 kg / sq. m;
- ceramoculepice - from 35 to 50 kg / square meters. m;
- cement tile - from 40 to 50 kg / kV. m;
- bituminous tile - from 8 to 12 kg / kV. with;
- profile flooring and metal tile are the lightest - approximately 4-5 kg \u200b\u200b/ sq. m.
We should consider the weight of each material used in the construction of the cake, including the draft flooring, the crate and the rafter system. So, draft flooring usually weighs no more than 20 kg / sq. m, doom - from 8 to 10 kg, and a rafter system of wood - 15-20 kg / square meters. m.
To calculate the final load on the system, you must add all the above data.
It is useful to know: Most sellers of roofing materials make an emphasis on extremely low coverage weighing, arguing that this is one of its main advantages, they say, ease guarantees convenient installation, savings during transportation and reducing lumber spending for the solo system. In fact, the situation is exactly the opposite, and light roofing material can play against the customer. To refute the arguments of the sellers, make the calculation of the rafter system of the hip roof using different roofing materials.
To begin with, take the worst material from the above list - cement tile. She will cover our house in the Ivanovo region in the village of Babenki.
We already know that the snow load for this region is 189 kg / sq. m, the wind has a load of 24 kg / sq. m, the cement tile of the weight of 50 kg / sq. m, doomle - 20 kg, the rafter system will also be the maximum - 20 kg. After creating all the data, we obtain a total load on the rafter system of 303 kg / kV. m.
If you take the easiest roofing material - metal tile, then with its weight and similar loads, characteristic of the climate in the village of Babenki, the load on the rafter will be 258 kg / sq. m.
Differences in the calculated loads constitute only 15%, so there can be no speech about any significant savings on sawn timber. In addition, in the chapter on wind load, we found out that the harder the roof is, the more difficult the wind will disrupt its integrity.
Now that we have dealt with how to calculate the total load on 1 square meters. m roofs, you can proceed to the calculation of the rapid system itself.
Calculation of the rafter system
Since the rafter system is a "skeleton", consisting of individual elements, then to determine the total load on it, it is necessary to find out which load is experiencing each of the elements - rafting legs.
To do this, it should be found a distributed load on a 1-line meter of each rafter by formula: QR \u003d A * Q, where QR is a distributed load on the pattern meter of each element (measured in kg / sq. M), q is a total load for 1 kV. m roofs, a - distance in meters between the rafters (step rafted).
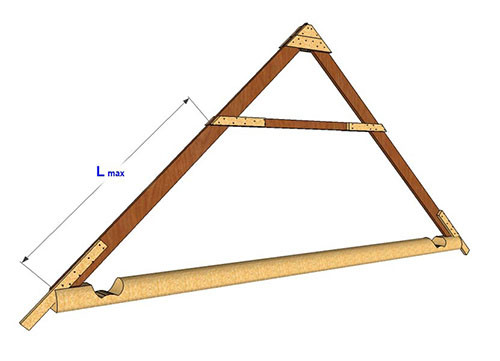
Next, you should find the maximum long working plot on the rafter foot (shown in the figure):
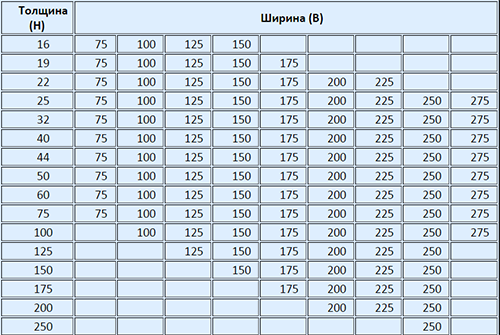
To properly select the material for the manufacture of the rafter system, use the table sizes table:
To calculate the cross section of the rafter arbitrarily set its width in accordance with the rated dimensions, and find the height of one of the following formulas according to one of the following formulas:
- H ≥ 8.6 * LMAX * SQRT (QR / (B * RIPS)), when the roof is biased, 30 ° or less;
- H ≥ 9.5 · LMAX · SQRT (QR / (B · RIPS)), when the roof is incidence of 30 ° or more.
Here H is the height of the section and is measured in cm, Lmax is the maximum long working portion of the rafter (measured in M), QR is a load on 1 phenon M of the rafal (measured in kg / m), B is a sequence width, SQRT. root, and RIZG is the resistance of the bending tree (measured in kg / sq. M. cm). At the same time, each breed of wood has its own RIZG. Since it is most often used for the construction of rafters, it is 140 kg / sq. cm (1 grade), 130 kg / kV. cm (2 grades) and 85 kg / kV. cm (3 grades).
The nominable wood deflection under load of the whole roof cannot be higher than the value of L / 200 (L is the length of the working segment in cm). Check whether the deflection degree corresponds to the norm by providing the loyalty of inequality:
3,125 * QR * (LMAX) ³ / (b * h³) ≤ 1
Recall that B and H is the width and height of the section, respectively (measured in cm). If the inequality is not respected, these two indicators should be increased.
For example, we will calculate the rafter system in the house located in the Ivanovo region with a roof slope of 36 ° (α), a step of rafted 0.8m (A), the maximum long working segment of 2.8 m (LMAX). Since we used 1 grade pine, then RIZG will be 140 kg / sq. See as roofing, we took a heavy and reliable cement tile with a load of 50 kg / sq. m.
We already know the total load per square meter. m of such a roof - it is equal to 303 kg / sq. M (Q). Now you can find a distributed load by 1 Raman M of each element of the system: QR \u003d A * Q;
QR \u003d 0.8 * 303 \u003d 242 kg / m.
Suppose the width of the chalkboard for a rafter foot is 5 cm, respectively, the width of the section for calculation will be equal to 5 cm. Since the inclination of the roof exceeds 30 °, select the formula H ≥ 9.5 * LMAX * SQRT (QR / B * RIPS), we substitute the values and we obtain H ≥ 9.5 * 2.8 * SQRT (242/5 * 140).
H ≥15.6 cm.
Taking advantage of the table above, we select the board with the most suitable cross section - its height will be 17.5 cm, and the width is 5 cm.
Now it remains to check whether the magnitude of the deflection corresponds to the norm. We substitute the values \u200b\u200bin the inequality 3,125 · qr * (lmax) ³ / b * h³ ≤ 1 and we get 3,125 * 242 * (2.8) ³ / 5 * (17,5) ³ \u003d 0.61. Since 0.61 is less than 1, then the cross section of the rafter we chose true.
Let's summarize: in our house, it is necessary to install rafters with a width of 5 cm, 17.5 cm high every 0.8 m.
As you have already done to make sure, to perform a competent calculation, it is necessary to operate with many values \u200b\u200band accurately know the weight of materials, various loads, climatic conditions, etc. If you are not sure about your abilities, it is better to attract a specialist, since it is not worth saving on such an important question. In particular, if we are talking about complex structures - the calculation of the rafter system of the four-page roof newcomer will correctly be extremely difficult. Fortunately, today you can use automatic programs that allow you to unmistakably calculate the necessary data. For example, the Arcon program enjoys many professional roofers to speed up the work process and avoiding errors.
Finally, we suggest you familiarize yourself with the training video material for the installation of a rafter system: